Three Nutritional Differences Between Bananas And Food Bananas

Bananas and bananas are fruits that come from countries with tropical and warm climates.
They are usually considered as a staple food in the daily diet of many populations and they provide a large amount of benefits to those who consume them.
These fruits have a similar appearance and come from the same plant family: Musaceae. They are also used in different ways when it comes to cooking – whether they are fried, cooked, baked, grilled or just eaten raw.
This is not only because of their small differences in texture and taste, but also because of their nutritional values that they make up two different fruits.
If you want to learn the difference between bananas and food bananas, also called plantans, we suggest you continue reading this article. Do not miss it!
Food bananas
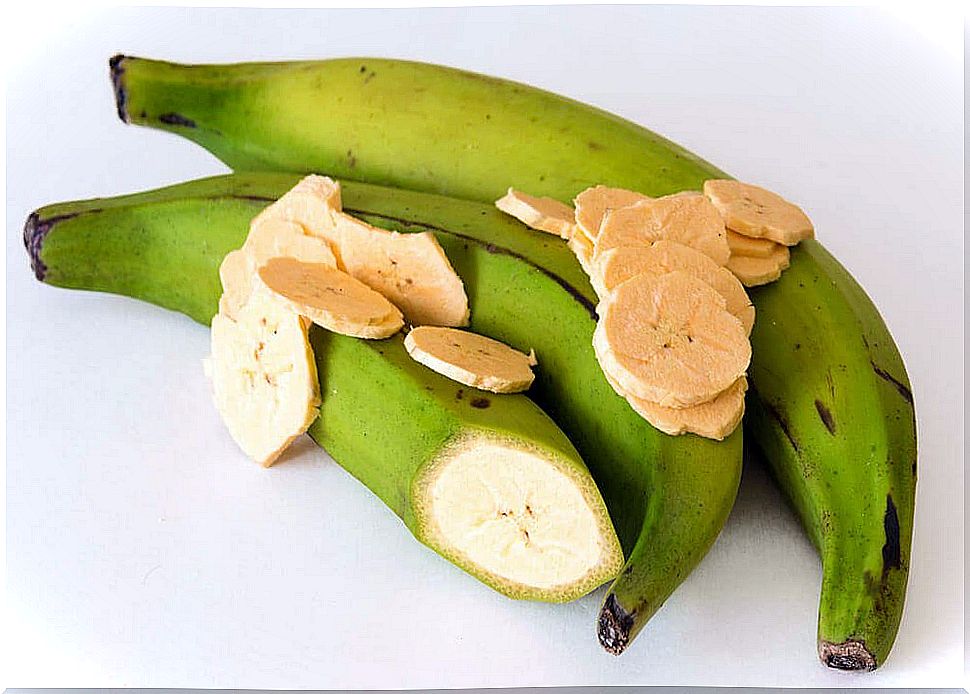

As we have already mentioned, food bananas are a fruit that comes from the Musaceae family, more specifically the paradisiacal type.
Because of this, they can be easily found in tropical countries, especially those close to the coast where it is very hot, such as Mexico, Ecuador, Brazil and Costa Rica.
The main characteristics of this fruit are its long shape and green peel, which turns yellow when it ripens, and black when it is past its maturity.
The nutritional value of 100 grams of a food banana is:
- Energy value: 96.4 kcal
- Fiber: 2.5%
- Calcium: 7.8 mg
- Magnesium: 38.5 mg
- Iron: 0.3 mg
- Copper: 0.1 mg
- Zinc: 0.2 mg
- Manganese: 0.1 mg
- Vitamin: C 17.5 mg
- Protein: 1.7%
- Potassium: 490 mg
- Phosphorus: 59.1 mg
- Carbohydrates: 22.5%
All these properties make the food banana a juicy fruit when ripe. But they also contain a lot of starch, which contains carbon, oxygen and hydrogen.
The starch prevents you from eating bananas until you cook them because they are astringent, gummy and dry.
- Generally, when green, they can be boiled in hot oil or water.
- If it is ripe or yellow, you can also cook it in the oven or on the grill.
Bananas

Bananas also belong to the family Musaceae, but it is of the acuminate type. They are most commonly grown in countries such as Uganda, Ecuador, the Philippines and Brazil.
Their main properties are their cylindrical, soft and smooth shape. They are white on the inside with a green peel that turns yellow as they mature.
The nutritional value of 100 grams of a banana is:
- Energy value: 110.15 kcal
- Fiber: 2.3%
- Calcium: 12.5 mg
- Magnesium: 41.5 mg
- Iron: 0.9 mg
- Copper: 0.3 mg
- Zinc: 0.2 mg
- Manganese: 0.1 mg
- Vitamin C: 18.5 mg
- Protein: 0.3 mg
- Potassium: 434 mg
- Phosphorus: 59.1 mg
- Carbohydrates: 26.2%
Unlike food bananas, bananas do not contain starch, so they can be eaten without having to be cooked first.
In addition, they are also known all over the world for their sweet taste and creamy texture. This makes them one of the best foods to eat at any time of the day.
Differences between bananas and food bananas

Despite having almost the same properties, bananas and edible bananas can be separated with greater precision when it comes to:
1. Microminerals
Food bananas contain a smaller amount of microminerals than bananas, such as:
- Iron
- Copper
- Zinc
- Manganese
- Sodium
But they contain more potassium, which contains 63.3 grams for every 100 grams of fruit.
They also contain more sodium, with bananas having 2 grams for every 100 grams of total weight.
2. Calories
Food bananas contain more calories, with 90 for every 100 grams of fruit.
This makes bananas a better solution when it comes to keeping a healthy diet low in calories.
3. Protein
Although bananas have a low calorie content, food bananas have four times its amount of protein, vitamin A and iron. This makes it a better option to give your body a greater amount of nutritional benefits.
Bananas give us many benefits when it comes to losing weight. But as we have seen, food bananas are able to give us more beneficial properties.
Food bananas also provide more vitamins and minerals to those who eat them.