Characteristics Of Osteosarcoma In Children
Osteosarcoma in children accounts for 3% of all cancers that occur in children. It is the most common type of bone cancer and one of the few that begins directly in the bone tissue. Unfortunately, it can spread to other areas of the body.
The survival rate for osteosarcoma in children is about 60 to 80% when it does not spread beyond the first tumor. Of course, it depends on the effectiveness of the chemotherapy. On the other hand, the chances of survival are much lower if it has already spread to other areas.
According to estimates, osteosarcoma represents about half of all cases of this disease in children. Most diagnoses occur between the ages of 10 and 30 years. In addition, it is more common in adolescents.
What is osteosarcoma?
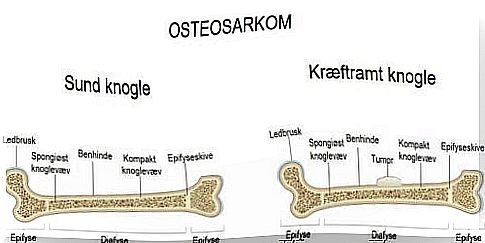
This is a form of cancer that develops in bone cells. It is also known as osteogenic sarcoma and manifests itself as a malignant tumor that can spread to almost any part of the body – most often first to the lungs.
This type of cancer usually begins at the ends of the bones in the arms or legs, but also affects other bones. It usually grows in the following areas :
- The top of the knee or the distal femur.
- Below the knee or proximal tibia.
- Under the shoulder or proximal humerus.
Osteosarcoma usually occurs in children older than 10 years. Some believe that this cancer is due to DNA failure in bone cells in the stages of intense growth. In general, it affects boys more than girls, and most cases occur in the knee.
Types of osteosarcoma in children
There are essentially two types of osteosarcoma in children and adults. Each of them contains several subtypes:
- A central tumor, also known as a medullary tumor, occurs deep in the bone
- Conventional central osteosarcoma
- Telangiectatic
- Intraosseous, well-differentiated or low-grade
- Small cell osteosarcoma
- A superficial or peripheral tumor occurring in the lower areas
- Parosteal osteosarcoma is also known as juxtacortical
- Periosteal
- Superficial osteosarcoma or high-grade
Risk factors
In general, osteosarcomas occur in people who have neither other diseases nor a family history of bone cancer. All indications are that a set of genetic changes that lead to the disease happens at random.
That said, note that in some cases, there are factors that promote the development of the disease. Among them:
- Previous radiation therapy for other cancers; especially at a young age
- Hereditary retinoblastoma
- Previous diseases such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Werner syndrome and Rothmund-Thomson syndrome
Symptoms of osteosarcoma in children
The symptoms of osteosarcoma vary. In fact, some patients are asymptomatic. However, some of the most common manifestations are:
- Pain in a bone or joint, which increases with time until it becomes unbearable.
- Broken bones, for no apparent reason.
- The presence of a mass or lump.
- Loss of bowel or bladder control.
- Back pain.
As you can imagine, it is important to be aware of the occurrence of one of these symptoms, especially in adolescence. Do not hesitate to consult a specialist if you suspect it in any way.
Diagnosis and treatment
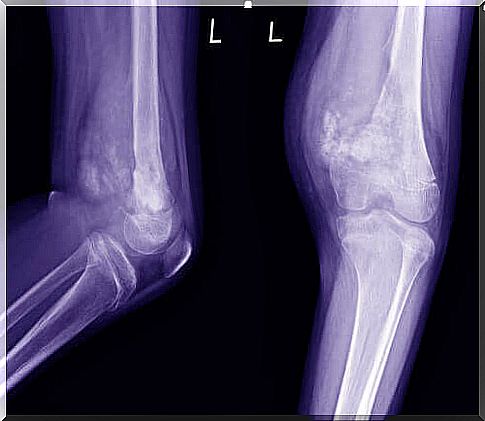
The diagnosis is usually made on the basis of a clinical interview and health history along with some tests. It usually starts with X-rays, which are supplemented with an MRI scan. A doctor will perform a biopsy as soon as they discover a problem and identify the area.
After confirming the diagnosis, the doctor will order a CT scan of the breast, a bone scan and sometimes more MRI scans. All this allows them to make a more accurate diagnosis and determine a more effective treatment.
The treatment of osteosarcoma in children includes chemotherapy and aims to shrink the cancerous nodule. Afterwards, surgery will be necessary to remove the tumors, and finally, they will treat the patient with chemotherapy again to minimize the likelihood of recurrent cancer.
Look for symptoms of osteosarcoma in children
As you can see, osteosarcoma can occur subtly and without previous cases in children. In addition, parents should be aware of the occurrence of possible symptoms, especially in adolescence.
Finally, contact a specialist to rule out this and other possible pathologies that could seriously affect your health if you suspect your child may have an illness.